by Tim Rowan, Editor Emeritus
Lawsuits are beginning to pile up against insurance companies participating in the Medicare Advantage program. The complaint? The wrong way to use AI in healthcare is with faulty algorithms to approve or deny claims. While AI can be extremely helpful in streamlining administrative tasks — comparing physician notes with Home Health assessments and nursing notes or reading hospital discharge documents — it seems not to be any good at deciding whether to approve or deny care.
The Wrong Way to Use AI in Healthcare Example 1
The Minnesota case, November, 2023, UnitedHealth Group:
-
- An elderly couple’s doctor deemed extended care medically necessary
- UnitedHealth’s MA arm denied that care
- Following their deaths, the couple’s family sued UnitedHealth, alleging:
- Straight Medicare would have approved the extended care
- United uses an AI model developed by NaviHealth called nH Predict to make coverage decisions
- UnitedHealth Group acquired NaviHealth in 2020 and assigned it to its Optum division
- nH Predict is known to be so inaccurate, 90% of its denials are overturned when appealed to the ALJ level
- UnitedHealth Group announced in October, 2023 that its division that deploys nH Predict will longer use the NaviHealth brand name but will refer to that Optum division as “Home & Community Care.”
The family’s complaint stated, “The elderly are prematurely kicked out of care facilities nationwide or forced to deplete family savings to continue receiving necessary medical care, all because [UnitedHealth’s] AI model ‘disagrees’ with their real live doctors’ determinations.”
The Wrong Way to Use AI in Healthcare Example 2
The Class-Action case, December 2023, Humana:
-
- A lawsuit was filed on December 12, 2023 in the U.S, District Court for the Western District of Kentucky
- It was filed by the same Los Angeles law firm that filed the Minnesota case the previous month, Clarkson
- The suit notes that Louisville-based Humana also uses nH Predict from NaviHealth
- The plaintiffs claim, “Humana knows that the nH Predict AI Model predictions are highly inaccurate and are not based on patients’ medical needs but continues to use this system to deny patients’ coverage.”
- The suit says Medicare Advantage patients who are hospitalized for three days usually are eligible to spend as many as 100 days getting follow-up care in a nursing home, but that Humana customers are rarely allowed to stay as long as 14 days.
- A Humana representative said Humana their own employed physicians see AI recommendations but make final coverage decisions.
What Makes This Possible
According to experts we speak with, there are many ways to use data analytics. The insurance companies named in the lawsuits use predictive decision making. This way of analyzing data compares a patient to millions of others and deduces what treatment plan might be suitable for one patient, based on what was effective for most previous patients. Opponents of this method have called it “data supported guessing.”
A superior analysis method experts are coming to understand is prescriptive decision making. This is taking all of the available historical and current data surrounding a patient and making a clinical decision specifically designed to that patient’s age, gender, co-morbidities, doctor recommendations, and treatment records.
Until recently, predictive analysis was the preferred method because of its resource efficiency. Examining the data of every individual patient used to be prohibitively labor-intensive, requiring hours of reading hospital records, physician notes, and claims. Today, however, AI tools are able to do that work in seconds, making prescriptive analytics and customized plans of care possible.
Fix May Be in the Works
In a February 6, 2024 memo to all Medicare Advantage Organizations and Medicare-Medicaid Plans, CMS explained the difference between predictive and prescriptive analytics. The memo said these plans may not make coverage determinations based on aggregated data but must look at each individual:
“For Medicare basic benefits, MA organizations must make medical necessity determinations in accordance with all medical necessity determination requirements, outlined at § 422.101(c)1 ; based on the circumstances of each specific individual, including the patient’s medical history, physician recommendations, and clinical notes; and in line with all fully established Traditional Medicare coverage criteria.”
In response to a request for clarification, the CMS memo laid out its rule in specific language: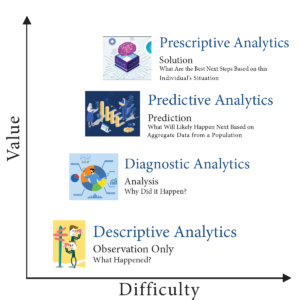
An algorithm or software tool can be used to assist MA plans in making coverage determinations, but it is the responsibility of the MA organization to ensure that the algorithm or artificial intelligence complies with all applicable rules for how coverage determinations by MA organizations are made. For example, compliance is required with all of the rules at § 422.101(c) for making a determination of medical necessity, including that the MA organization base the decision on the individual patient’s circumstances, so an algorithm that determines coverage based on a larger data set instead of the individual patient’s medical history, the physician’s recommendations, or clinical notes would not be compliant with § 422.101(c).
(emphasis added)“Therefore, the algorithm or software tool should only be used to ensure fidelity with the posted internal coverage criteria which has been made public under § 422.101(b)(6)(ii).”
In further responses to questions in the same memo, CMS made it clear MA plans must make the same coverage decision original Medicare would make. The only allowable exception is that plans may use their own criteria when Medicare Parts A and B coverage criteria “are not fully established.”
Knowledge of this CMS directive may give Home Health agencies one more arrow in their quiver when going to battle with powerful, profit-oriented insurance companies over harmful, illogical AI algorithm decisions.
For information on the right way to use AI in healthcare, see our complimentary article in this week’s issue.
Tim Rowan is a 30-year home care technology consultant who co-founded and served as Editor and principal writer of this publication for 25 years. He continues to occasionally contribute news and analysis articles under The Rowan Report’s new ownership. He also continues to work part-time as a Home Care recruiting and retention consultant. More information: RowanResources.com
Tim@RowanResources.com
©2024 by The Rowan Report, Peoria, AZ. All rights reserved. This article originally appeared in Healthcare at Home: The Rowan Report.homecaretechreport.com One copy may be printed for personal use: further reproduction by permission only. editor@homecaretechreport.com



